Ball valves are ideal for conveying media of extreme types due to their extremely adaptable design features. Ball valves must therefore have specific safety features in order to avoid any hazards in the plant. These five safety characteristics are the most important ones for ball valves.
A ball valve is a shut-off mechanism that uses a revolving ball with a hole to control the flow of a liquid or gas. The valve can be opened or closed to let the medium pass through or to prevent it by rotating the ball 90 degrees, or a quarter revolution, around its axis. Even when left idle for lengthy periods of time, ball valves are renowned for their long lifespan and reliable sealing. Compared to the majority of other valve types, they are more resilient to contaminated media.
Ball valves are perfect for flammable and corrosive applications because of their high temperature and high pressure characteristics and their fabrication from stainless steel. Ball valves are a dependable option for conveying hazardous gases because they provide efficient bubble-tight cutoff. Oil, gas, petrochemical, and chemical industries all use ball valves to move media.
What are the five Safety Features of Ball Valves?
The safety features in ball valves are:
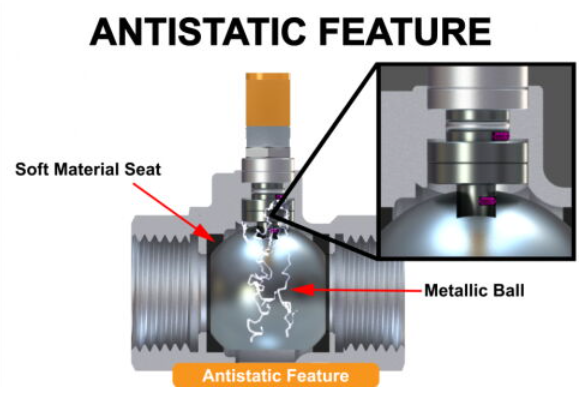
Ball valves' anti-static design is an essential safety element that keeps static electricity from building up while the valve is in operation. This optional ball valve design has anti-static components between the ball and stem and between the stem and body. This ensures that all of the valve's metal components are grounded and lowers the possibility of fire dangers brought on by the accumulation of static charges.
One of ball valves' most important safety features is their anti-static construction, which helps stop static electricity from building up while the valve is operating. The anti-static components of this optional ball valve design are positioned between the ball and stem and between the stem and body, guaranteeing that the valve's metal components are completely grounded.
The friction between the soft seat and the ball during a ball valve's operation can produce static electricity. There is a significant chance that this static charge will ignite flammable substances inside the valve, perhaps causing a fire.
Ball valves can be equipped with an anti-static device to mitigate this risk. A stainless steel ball and a spring are usually used in this device, which creates a continuous grounding channel from the ball to the stem and from the stem to the body and ground. This lowers the chance of a fire by ensuring that any static charge produced during operation is securely released.
In conclusion, a crucial safety element that can lessen the risk of fire dangers brought on by static charge accumulation is the anti-static design of ball valves. Although this function is optional, it is strongly advised for applications where the accumulation of static electricity is an issue.
What is an industrial ball valve that is fire-safe? One kind of industrial valve designed to resist high temperatures is a fire-safe industrial ball valve. These valves close tightly to stop leakage when exposed to fire. This safety element is particularly crucial for systems that deal with explosive or flammable chemicals.
The majority of industrial ball valves have soft seals as their main seal, which are frequently composed of Teflon or similar materials. Under normal circumstances, these soft seals produce a tight closure, but under extremely hot temperatures, they may melt or fail. By employing a backup metal seal that kicks in in the event that the soft seal fails, fire-safe valves provide an additional degree of security.
Extreme heat can be tolerated by the long-lasting metal-to-metal seal. Because of this feature, combustible liquids can't escape and fuel a fire. In industries with a high danger of fire, fire-safe valves are crucial. This is because they assist control dangerous situations and limit harm.
Before being approved, fire-safe valves must pass stringent testing. Testing guarantees that the valve can operate as intended in the event of a fire. Users can feel secure knowing that the valve will function in an emergency thanks to these requirements.

The purpose of the anti-blowout stem feature is to prevent the stem from being forced out of the valve body by the inline pressure. By including an inverted T-shaped shoulder design for the stem, which is then inserted from inside the valve body, the anti-blowout stem feature is accomplished. The following is a precise explanation of the principle:
When the valve is in the open or closed state, the internal pressure constantly tries to force the stem upward. The stem housing, which is fastened to the body, holds the o-rings and graphite packing rings that seal the stem in place. Thus, even when the valve is under pressure, the stem will be held firmly by the stem housing when we remove the gland flange to replace the graphite packing rings.

Ball valves have an emergency sealant injection mechanism as a safety feature to provide sealing at the stem and seats in the event of a leak. In order to provide a barrier that reduces leakage across the valve, ball valves are equipped with a sealant injection mechanism. The ball valve's stem and seat area are equipped with sealant injection fittings. They may serve as a short-term seal.
Grease or lubricant injection fittings can be used to inject grease or sealant when the soft sealing is compromised and a leak occurs due to fire incidents. To stop additional leaks, the injected sealant acts as a temporary closure.
However, it should be remembered that the sealant injection method is only meant to be used in an emergency. By drawing in more oil and debris, the process of injecting grease through sealant injection fittings raises the possibility of additional damage to the ball valve seat.

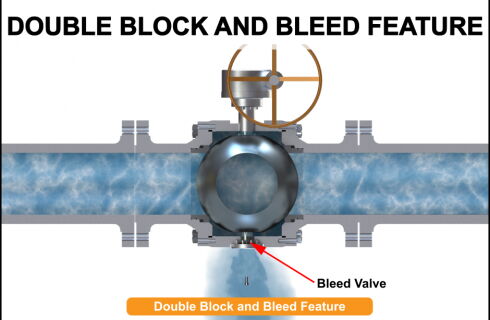
The double block and bleed feature is a safety feature that keeps the process media away from the other downstream equipment by achieving a firm shutoff in the ball valve. By employing a bleed valve to remove the media in the space between the two seats, the pressure on the seats is released. When a ball valve is closed, the two pressure-energized seats function as two separate block valves.
Double block and bleed (DBB) valve has two isolation barriers and a way to vent or bleed the space between them. This setup is intended to improve safety and streamline fluid or gas system maintenance processes.
Two block valves and a bleed (or vent) valve are usually the primary parts of a double block and bleed valve:
1.The main isolation valves are block valves. In a double block and bleed valve, there are two of them. To isolate a portion of the pipeline or system, these valves can be closed.
2.Between the two block valves is a valve known as the Bleed (Vent) valve. The fluid or gas that is trapped between the two block valves is released or bled using it. This guarantees that any remaining pressure is securely released prior to doing any maintenance.