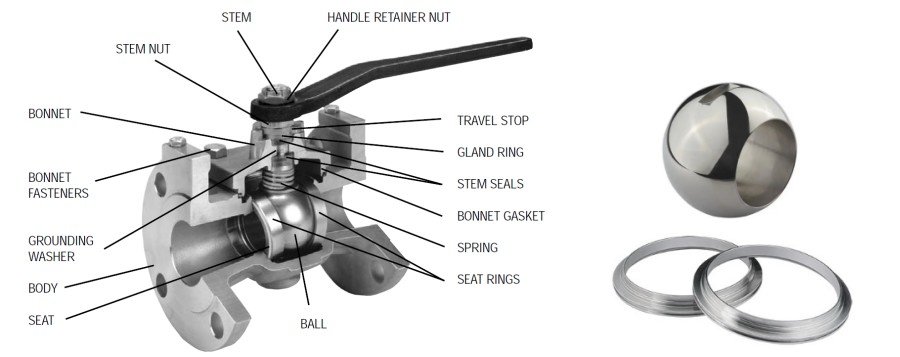
Metal Seated Ball Valve is manufactured for high temperature up to 540℃ (may be higher based on the material of body and trim) or abrasion resistance. For metal seated ball valve, the seat ring and ball are precisely machined, coated by high velocity oxygen fuel(HVOF) coating process and lapped to match ball, creating a positive seal for bubble-tight performance. Metal seated ball valve provide long service life with outstanding fugitive emissions performance and low operating torques in even the toughest applications.
The hardening of metal seated ball valves is important for several reasons. First and foremost, it enhances the valve's resistance to wear and tear, ensuring its durability and longevity. The ball and seat of the valve are subjected to high pressures and repeated cycles of opening and closing, which can cause erosion and damage over time. By hardening the surfaces, the valve becomes more resistant to these effects, increasing its lifespan.
Additionally, hardening improves the valve's ability to withstand harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments. This is especially crucial in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, or power generation, where valves are exposed to extreme conditions. Hardening the metal surfaces helps prevent deformation, erosion, and chemical reactions that could compromise the valve's performance.
Furthermore, a hardened metal seat provides a better sealing capability. When the valve is closed, the metal seat forms a tight seal with the ball, preventing any leakage. Hardening the seat ensures a smoother and more precise sealing surface, reducing the chances of leakage and improving the valve's efficiency.
Overall, the hardening of metal seated ball valves is essential for their longevity, resistance to harsh conditions, and reliable sealing performance. It helps ensure smooth operation, minimize maintenance requirements, and increase the valve's overall reliability in various industries.
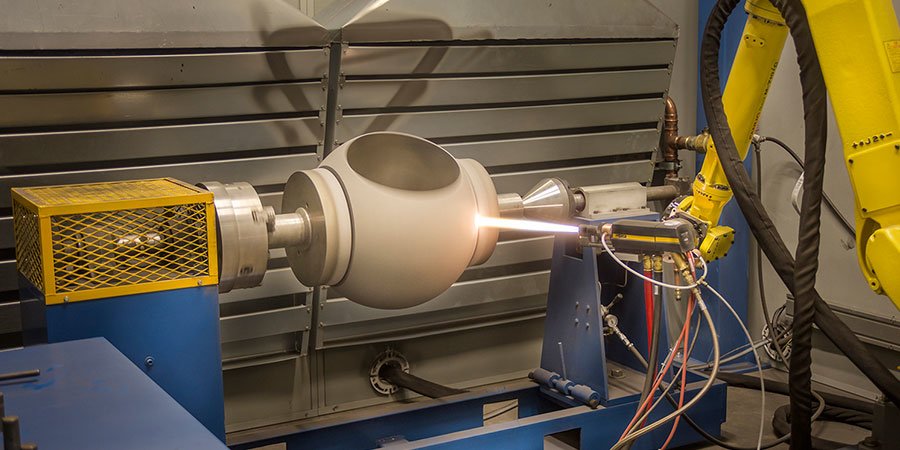
The steps of hardening process of a metal-seated ball valve
The hardening process of a metal-seated ball valve typically involves a few steps to enhance its durability and resistance to wear. Here's a general overview of the process:
1. Material Selection: The first step is to choose the right metal alloy for the valve body, ball, and seat. Common materials used include stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloys like Inconel or Monel, depending on the application requirements.
2. Heat Treatment: Heat treatment is often applied to improve the mechanical properties of the metal. This process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it in a controlled manner. Heat treatment techniques like annealing, quenching, or tempering may be used.
3. Surface Hardening: To further increase the hardness and wear resistance of the valve components, surface hardening techniques are employed. Common methods include:
a. Nitriding: The valve components are exposed to a nitrogen-rich environment at high temperatures, which forms a hardened layer on the surface by diffusion.
b. Hardening Coatings: Various coatings like tungsten carbide, chromium carbide, or ceramic coatings can be applied to the valve components through processes like thermal spray or physical vapor deposition (PVD).
4. Precision Machining: After the hardening process, the valve components undergo precision machining to achieve the desired dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish. This step ensures proper fit and functionality of the valve.
5. Assembly: Once the individual components are prepared, they are assembled into the final metal-seated ball valve. This involves carefully fitting the ball and seat, ensuring proper sealing and smooth operation.
It's important to note that the specific hardening process may vary depending on the manufacturer, valve design, and application requirements. Therefore, it's always recommended to consult the valve manufacturer's documentation or guidelines for precise details on the hardening process used for a particular metal-seated ball valve.
Next: Some information About Duplex Steel Valve
Previous: Y-strainer vs T-strainer
